
According to ZipRecruiter, the salary range for an entry-level instructional designer is between $50,000 and $60,000. A mid-level instructional designer’s salary range is $75,000-$85,000, and a senior-level instructional designer’s salary range is between $95,000 and $105,000. Learning theories are evidence-based models that attempt to explain, model, and predict how people learn. (It is important to note that different learning theories may also operationalize learning differently from one another.) There are many learning theories; three overarching learning theory paradigms will be reviewed here. Ideal approaches to discovery engage the use of interviews and agile project (or team) charters.
Key Components of Instructional System Design
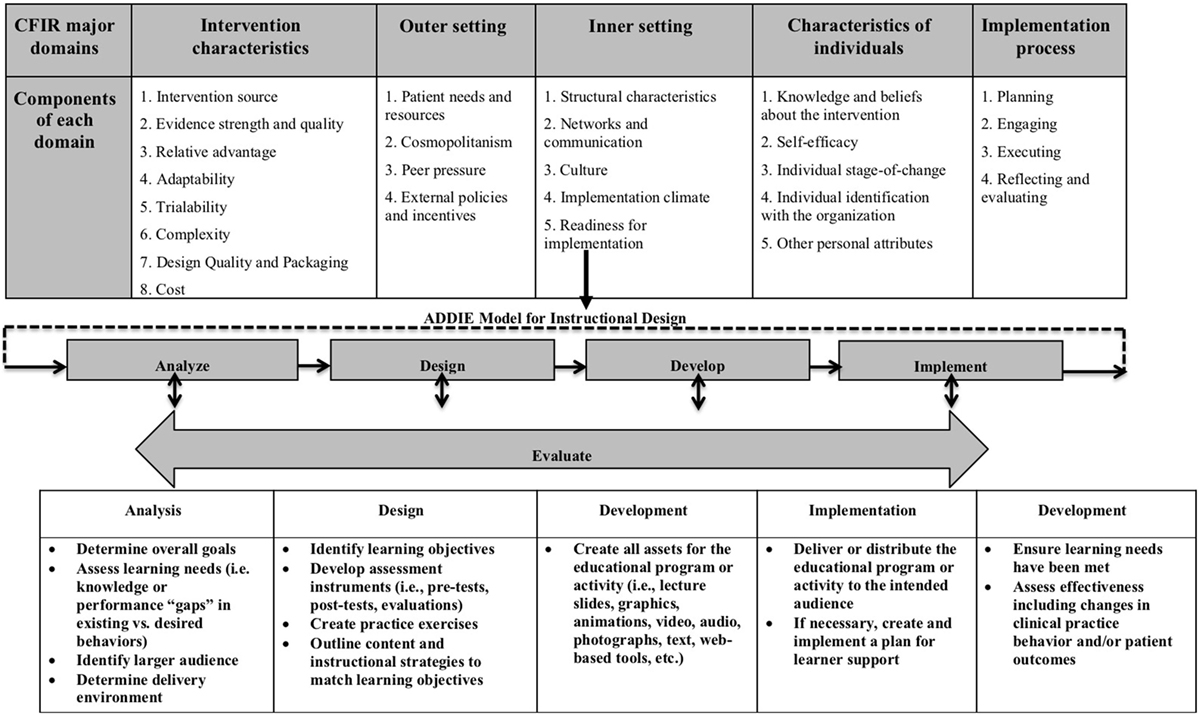
The design phase deals with learning objectives, assessment instruments, exercises, content, subject matter analysis, lesson planning and media selection. Systematic means a logical, orderly method of identifying, developing and evaluating a set of planned strategies targeted for attaining the project’s goals. Specific means each element of the instructional design plan needs to be executed with attention to details. Instructional System Design (ISD) is a systematic and disciplined approach to growing powerful and efficient educational experiences. ISD presents a structured framework for designing instructional material that facilitates the most fulfilling optimal outcomes. Its number one aim is to enhance the learning experience by aligning content with specific goals and tailoring it to the desires and characteristics of the target audience.
Instructional Designer Jobs and Salary Guide
While perhaps the most common design model, there are a number of weaknesses to the ADDIE model which have led to a number of spin-offs or variations. Once an instructional designer analyzes the needs assessment and understands the training objectives, the course creation process can begin. The instructional design process requires selecting the most appropriate strategies, methodologies, learning activities, and technologies to maximize the learning experience and knowledge transfer. An instructional designer focuses on specific educational curricula to ensure they support the development of an organization’s learning environment.
MODULE 1: Introduction to ISD
A quality narrative is engaging, meaningful, and authentic, and puts the learner in the center of the problems. Quality narratives also are a natural fit with the content, learning objectives, and outcomes. It is not always easy to create a quality narrative, and doing so often requires conversation and collaboration within a team. By thinking through a typical scenario, the designer gains empathy for the learner, which in turn reveals the problems and helps to shape the design solutions that support the students.
Guaranteed Learning
Among the first to coin the term "instructional design", Gagné developed some of the earliest instructional design models and ideas. It is in striving for effectiveness (the ability to achieve learning outcomes) that designers draw upon theory and understanding of human learning, motivation, and key principles of instructional design. Educator, researcher, and instructional technologist, David Merrill, advocated a simple instructional design model that acknowledges problem-solving as the root of effective learning experiences. MPI focuses on five core principles – problem-centric, activation, demonstration, application, and integration – to guide ID professionals in their instructional systems design efforts. MPI-based learning delivers value to the organization because learners don’t just gain knowledge, they also learn how to apply it to solve workplace problems.
Gagne’s Nine Events of Instructions
This model attempts to save time and money by catching problems while they are still easy to fix. Gagné's main focus for instructional design was how instruction and learning could be systematically connected to the design of instruction. He emphasized the design principles and procedures that need to take place for effective teaching and learning. Instructional designers help identify gaps in existing curriculums, student engagement, and teaching methods and look for solutions to bridge those gaps.
Make sure you explain to them that it’s OK to mess up, at least at first. As the material builds in complexity, always relate new material to previously learned material. Point out how the new material relates to the old—and how it points to what’s coming in later lessons. Use outlines and tables to organize hierarchical structures and diagrams to illustrate more complicated relationships among various components of the material.
How ATD Can Help You With Instructional Design?
For example, during the development of instructor-led materials, an Instructional Technologist may create drafts of instructor guides and student materials. In comparison, the development of computer or web-based instruction may require Instructional Technologists to create storyboards, flowcharts and electronic prototypes. Instructional Technologists developing instructional videotapes may produce camera shot sheets and scripts for actors. We will learn the primary process of task analysis including identifying learning goals and outcomes, conducting information processing analysis and prerequisites analysis, and developing learning objectives.
Fort Worth ISD considering $23 million compensation package that includes teacher raises - Fort Worth Report
Fort Worth ISD considering $23 million compensation package that includes teacher raises.
Posted: Wed, 14 Jun 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
While a completed blueprint may be linear in nature (e.g., progressing from Module 1 to Module 10), the process of creating it involves varying degrees of nonlinearity and iteration. For example, beginning with the final projects and assessments, followed by rubrics, then activities, and finishing with module and course introductions is not an uncommon workflow, especially with backward design (Wiggins & McTighe, 2011). Figure 10 illustrates how this process of ideation should ideally target ideas that are effective, meaningful, feasible, and sustainable, all while maintaining the vision and narrative. The implementation, or rollout, component entails delivering all content and materials (from the Design & Development phase) to trainers, for delivery to a targeted audience of learners. This component of the instructional systems design model also involves providing required training to instructors, trainers, and coaches, on how to use the content most effectively.
I hope this article can help you as well, with this proposed structure and a big picture of how an Instructional Designer should ideally work. Don't forget to send your course for feedback to your SMEs and your peers as well. Usually, the SMEs will review the content accuracy and your peers (other Instructional Designers) will review the design, media, and templates. A course that only requires students to remember information to spit back in a tightly controlled environment, such as a multiple-choice test or fill-in-the-blank, does its students a disservice. Instead, within the lesson structure, include opportunities for students to produce original content.
An important ingredient in efficiency is the format in which you design the system. Organise the material in a logical sequence that makes sense, depending on the material. For instance, for a history course design, the sequence might be chronological, while for literature themes might make better sense. Irrelevant information can distract the student from the main focus of each lesson. Infographics and other visual and audio aids should be easy to see and easy to understand. Develop – The third phase, Development, involves the creation of the activities that will be implemented.

No comments:
Post a Comment